The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act was enacted in 2012 by the Government of India to protect children from offences of sexual abuse, sexual assault, sexual harassment and pornography.
The act regards any person under the age of eighteen as a child. The welfare of the child is of paramount importance to ensure the healthy physical, emotional, mental and social development of the child.
The act also ensures that the child’s interests are safeguarded at every stage of the judicial process by incorporating child-friendly mechanisms for reporting, recording evidence, investigation and speedy trial of offences by designated special courts.
The act prescribes severe penalties for offences. The maximum penalty is life imprisonment and a fine.
Offences under the POCSO Act are:
- Penetrative sexual assault
- Sexual assault
- Sexual harassment
- Use of a child for pornographic purposes
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights
- The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) is mandated to monitor the implementation of the POCSO Act.
- NCPCR website
- POCSO website (NCPCR)
Instigating, abetting and attempting an offence of sexual abuse, sexual assault, sexual harassment and pornography are also punishable.
Offences are to be reported to the Special Juvenile Police Unit or the local police.
Anyone including a child can report an offence.
According to the POCSO Act, everyone is obliged to report the sexual abuse of a child. Failure to report or record is a punishable offence. However, a child cannot be punished for failing to report.
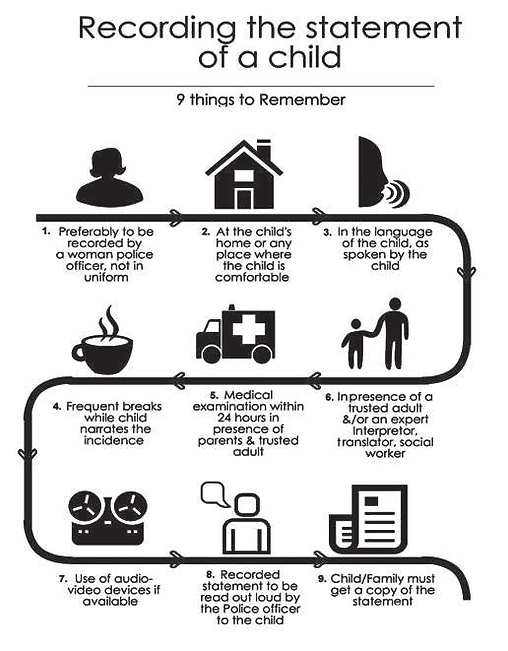
When recording a child’s statement, it is important to observe the following points.
Various punishable offences under the POCSO Act
- Penetrative sexual assault
Any form of penetration in private parts or other body parts or application of the mouth to the private parts of a child or forcing the child to penetrate the offender or someone else.
- Sexual assault
All acts of physical nature without penetration. For example stalking a child, showing dirty pictures, touching private parts of a child or making a child touch the private parts of someone else etc.
- Aggravated penetrative sexual assault
When penetrative sexual assault is committed by a person in a position of trust or authority such as police officer or a member of security forces or public servant etc.
- Aggravated sexual assault
Offences of sexual assault if committed by a person in a position of power, authority and trust or in certain circumstances.
- Sexual harassment and use for pornographic purposes
Sexual harassment is committed upon a child when such person with sexual intent:
- carries out any act with sexual connotations; or
- makes a child exhibit his/her body; or
- shows any object to a child in any form or media for pornographic purposes; or
- repeatedly or constantly follows or watches or contacts a child either directly or through electronic, digital or any other means; or
- entices or uses a child for pornographic purposes or gives gratification therefor.